
When you open your favorite food delivery app or log in to your banking portal, hundreds of background operations happen in milliseconds. Behind many of these actions lies a reliable workhorse — MySQL.
Whether it’s tracking your orders, managing your account data, or storing millions of transactions, MySQL quietly powers most of the web — from startups to global enterprises like Netflix and Airbnb.
Let’s break down why MySQL is such a powerhouse and how you can make the most of it — with simple, real-world examples.
What Makes MySQL the Backbone?
MySQL is an open-source relational database — meaning it organizes data into tables that are linked together using relationships.
Think of MySQL like a digital version of an Excel workbook:
- Each sheet = a table (e.g., Users, Orders, Payments)
- Each column = a data type (e.g., Name, Date, Amount)
- Each row = a record
But unlike Excel, MySQL can handle millions of rows, manage multiple users at once, and ensure data safety during crashes or power cuts.
A Real-World Example: Food Delivery App
Imagine you’re building a food delivery app like Zomato or Swiggy.
Here’s how MySQL fits in:
- Customers Table: Stores user details
- Restaurants Table: Stores partner restaurant data
- Orders Table: Tracks every order placed
- Payments Table: Logs transactions
When a customer places an order, MySQL ensures all these tables connect seamlessly using relationships like:
SELECT orders.id, customers.name, restaurants.name, orders.total_amount FROM orders JOIN customers ON orders.customer_id = customers.id JOIN restaurants ON orders.restaurant_id = restaurants.id;
This query shows one thing clearly — MySQL helps your data talk to each other efficiently.
Why MySQL Stands Out
- Easy to Learn – If you know basic SQL, you can start instantly.
- High Performance – Handles heavy read/write operations efficiently.
- Open Source – Free to use, with strong community support.
- Scalable – Works from a single laptop to AWS cloud clusters.
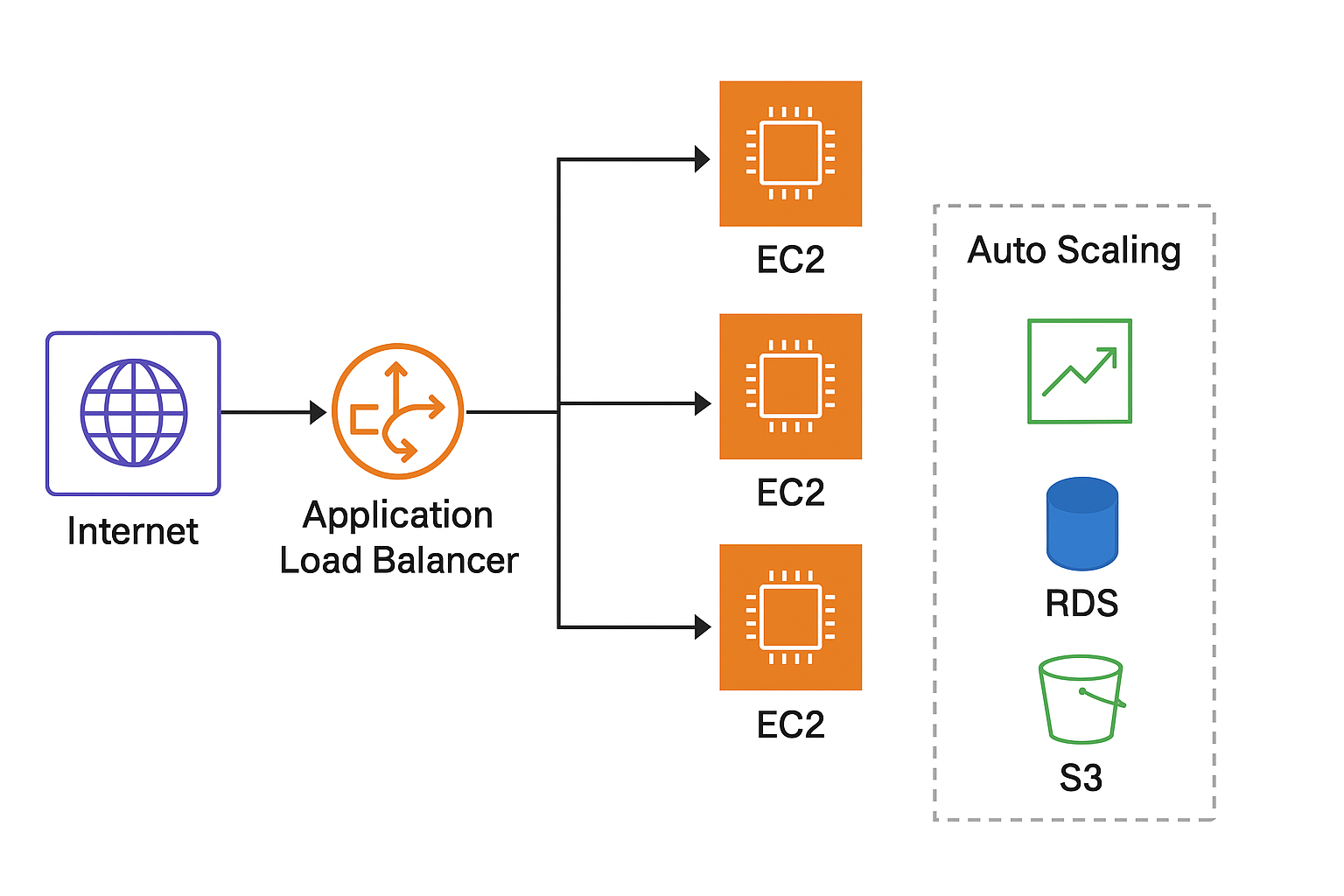
Scaling MySQL in Real-World Applications
When your app grows from 100 users to 10 million, MySQL still keeps up — but only if optimized properly.
Here’s how large systems handle it:
- Read Replicas – Copy your main database to handle more read queries.
- Load Balancing – Distribute requests between multiple MySQL instances.
- Partitioning – Split large tables (like “orders”) into smaller ones based on region or date.
💡 Example:
Amazon uses partitioning to separate order data by region, ensuring faster queries for both customers and admins.
Keeping Data Safe
Security is key in any application.
- Use prepared statements to prevent SQL Injection:
$stmt = $conn->prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ?");
$stmt->bind_param("s", $email);
$stmt->execute();
- Enable SSL connections for all database communication.
- Regularly back up your data using cron jobs or AWS RDS snapshots.
Monitoring and Tuning MySQL
Tools like AWS CloudWatch, Sentry, or Percona Monitoring help detect slow queries and track performance.
You can spot issues like:
- Long-running queries
- Locking during heavy traffic
- Memory usage spikes
A single slow query can impact thousands of users — so proactive monitoring is a must.
Final Thoughts
MySQL isn’t just a database; it’s the foundation layer that keeps your app running smoothly.
From storing customer details to managing transactions across servers, it continues to evolve — bringing performance, reliability, and simplicity together.
If you’re building any modern application — web or mobile — mastering MySQL is not optional. It’s essential.
No comments yet
Be the first to start the discussion!